|
Each
ACIS class derived from
ENTITY has an
identity method to allow applications and
ACIS to inquire the type of of an object, given an
ENTITY pointer to that object.
|
|
|
The
identity method accepts a single integer argument for the derivation level desired and returns an integer specifying the type of the object. The prototype for the
identity method is:
|
|
|
int identity(int level) const;
|
|
|
The
level argument is optional. If no
level
is specified, the most specific type of the object (greatest level of derivation) is returned.
|
|
|
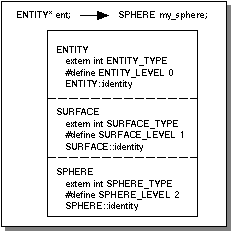
For example, if an object is defined of a class whose derivation is
sphere:SPHERE:SURFACE:ENTITY, and no
level is specified, the
identity function returns an integer whose value is
sphere_TYPE (which corresponds to
level=3). If level=2 is specified,
SPHERE_TYPE is returned. If
level=1 is specified,
SURFACE_TYPE is returned. This mechanism, along with the
C++ concept of polymorphism, allows a parent class to automatically call child methods where appropriate, and allows application code to determine the exact nature of the object being operated on. Refer to Figure 4-2.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 4-2. A SPHERE Object
|