|
Assemblies are a way of making complex parts that consist of repeated building blocks. For example, in steel frame manufacture, bolt groups frequently have to be modeled. It is highly advantageous to be able to model a single bolt and then
instance the bolt many times as though it were in the different locations that form the bolt group. Two benefits of assembly modeling are that model space is reduced and that many instances are modified by editing or replacing the body to which an instance refers.
|
|
|
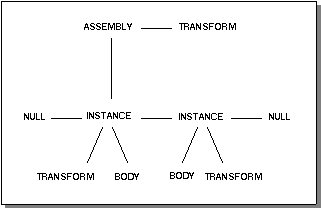
In the simple assembly example, an assembly contains a pointer to an instance and a transform. The transform allows the assembly to be moved cheaply with bodies. Each instance is made up of a pointer to a body and a transform. Instances are connected in a
NULL-terminated doubly-linked list. Refer to the diagram in Figure 8-1.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 8-1. Assembly Pointers
|
|
|
To model a car as an assembly, one might create two bodies,
CHASSIS and
WHEEL, and then five instances, one pointing to
CHASSIS and the other four pointing to
WHEEL. The transform pointed to by each instance arranges the assembly so that there is an instance of
WHEEL at each corner of the instance of
CHASSIS.
|